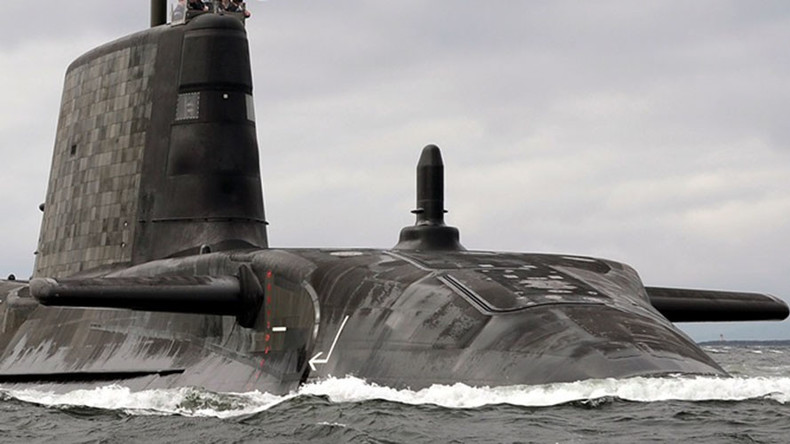
The Royal Navy is ‘cannibalizing’ boats for parts to complete the building of other ships, leaving established vessels without the capacity to sail. An investigation uncovered mass stripping of parts from across the whole fleet.
Nuclear-powered Astute-class hunter-killer submarines, some of the most modern and advanced vessels in the Royal Navy, experienced the highest level of cannibalisation in the fleet with 59 instances per boat on average.
Official guidance states that cannibalisation should only happen when no other solution is available, but the NAO said delays in deliveries of spares and a lack of information about when parts will be available contributed to the increase in the practice.
In the last five years, between 0.3% and 1.4% of parts provided to the main classes of ships and submarines have been cannibalised.
Between April 2012 and March 2017 there were 3,230 instances involving 6,378 parts, with 795 instances in 2016-17 alone – the equivalent of 66 a month, up from 30 a month in 2005.
The NAO report noted that in some circumstances, such as during high-intensity operations, cannibalisation can be the most effective way to keep vessels at sea.
But it can also lead to increased costs – in 50% of cases on Devonport-based Type 23 frigates the expense of moving equipment was equal to or greater than the value of the part – and risks causing damage or disruption.
“The risk of cannibalisation has increased further with reductions in fleet sizes meaning the armed forces have limited alternative equipment to deploy,” the report noted.
The NAO said the Ministry of Defence had taken decisions to cut support, which could have exacerbated the problem of cannibalisation.
“In the past two years, the Navy has removed an estimated £92 million from its maritime support in-year budgets,” the report said.
That amounted to 34% of the total £271 million of maritime support budget cuts.
In the Astute class, some parts were taken from submarines while they were still being constructed adding to delays in the production process and costing the taxpayer millions of pounds.
In the past five years, the three in-service Astute-class submarines had 506 defects, with 28% of the 313 resolved defects in 2016-17 fixed through cannibalisation, and the remainder by sourcing parts from the supply chain.
An average 1.4% of parts issued to Astute-class submarines involved cannibalisation compared with 0.4% across all ships and submarines.
An estimated £22 million of parts from submarines in production have been supplied to in-service parts and the practice delayed the completion of HMS Artful by six weeks, leading to an extra £4.9 million in indirect costs.
The NAO said the Ministry of Defence had identified that cannibalisation has affected submarines currently in production “leading to an estimated £40 million cost increase”.
A Royal Navy spokesman said: “Less than 0.5% of parts we use come from swapping components, and we only do this when it’s absolutely necessary to get ships out of port and back on to operations more quickly.
“We continue to make improvements to how we manage this long-established practice.”