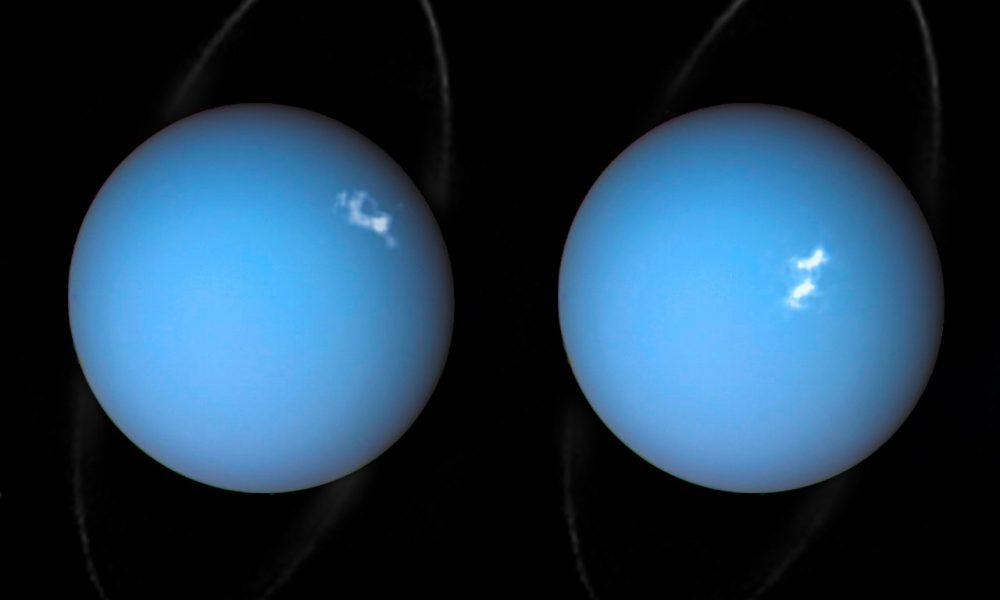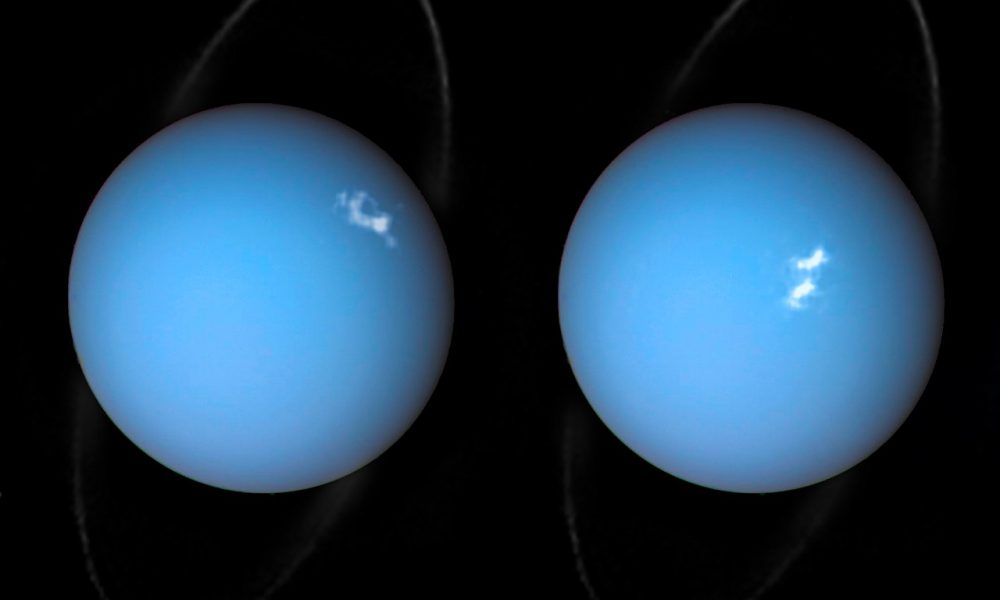
Nasa and the European Space Agency have released a stunning image showing auroras on Uranus.
Bright auroras light up the planet’s atmosphere in two newly released photos, which combine observations by NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope and the agency’s Voyager 2 probe. (Voyager 2 flew by Uranus in 1986 as part of a “grand tour” of the solar system’s outer planets that the spacecraft performed with its twin, Voyager 1.)
Uranus’ auroras are driven by the same basic processes that cause auroras here on Earth, which are also known as the northern and southern lights.
“Auroras are caused by streams of charged particles like electrons that come from various origins such as solar winds, the planetary ionosphere and moon volcanism,” NASA and European Space Agency (ESA) officials wrote in an image description (April 10). (Hubble is a joint NASA/ESA mission.)
“They become caught in powerful magnetic fields and are channeled into the upper atmosphere, where their interactions with gas particles, such as oxygen or nitrogen, set off spectacular bursts of light,” they added.
This isn’t the first Uranus aurora observation for Hubble; the telescope also captured them back in November 2011.
The newly released photos also show Uranus’ ring system, which appears to circle the planet’s poles. But the rings actually gird Uranus’ equator, just like those of Saturn: Uranus orbits the sun on its side, with the planet’s spin axis pointing nearly directly at the star. Astronomers think the gas giant was knocked off-kilter long ago by a collision with an Earth-size planet, or perhaps by a series of impacts with smaller objects.
Uranus is the third-largest planet in the solar system, with a diameter about four times that of Earth. Uranus lies about 19 times farther from the sun than our planet does, and it takes 84 Earth years to complete one orbit.
The Hubble telescope launched on April 24, 1990, aboard the space shuttle Discovery and was deployed a day later. The space telescope is still going strong, as is Voyager 2; the spacecraft, which launched in 1977, is currently about 12.8 billion miles (20.6 billion kilometers) from Earth and is expected to pop free into interstellar space soon. Voyager 1 entered interstellar space in August 2012 and is also still sending data home to its handlers.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6jSTbN_I_zk